-
Highlight
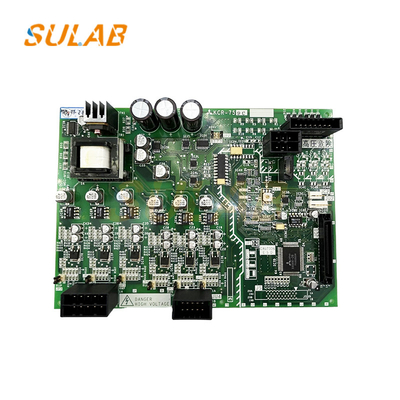
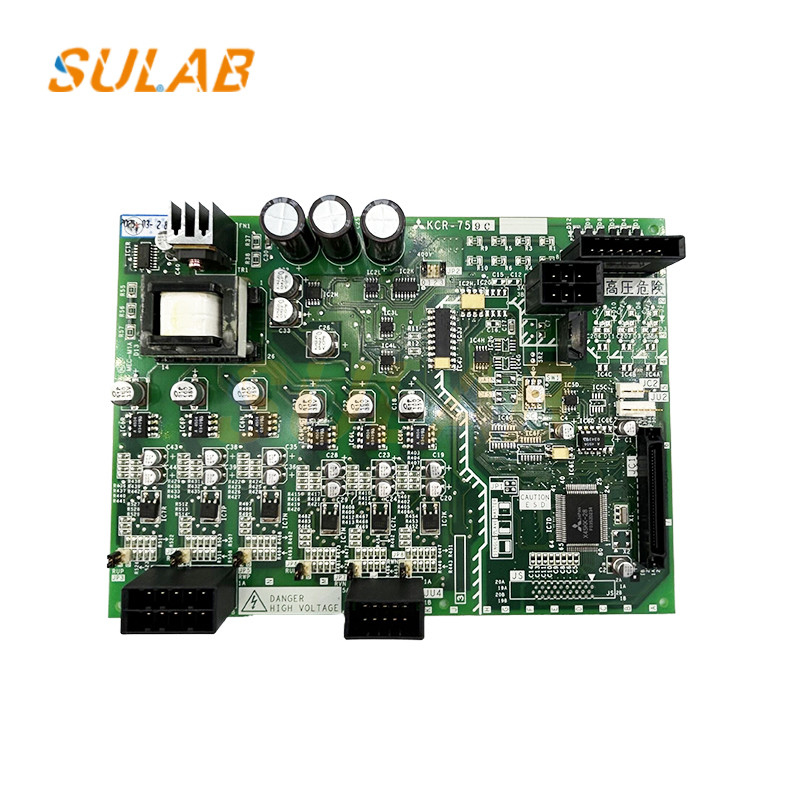
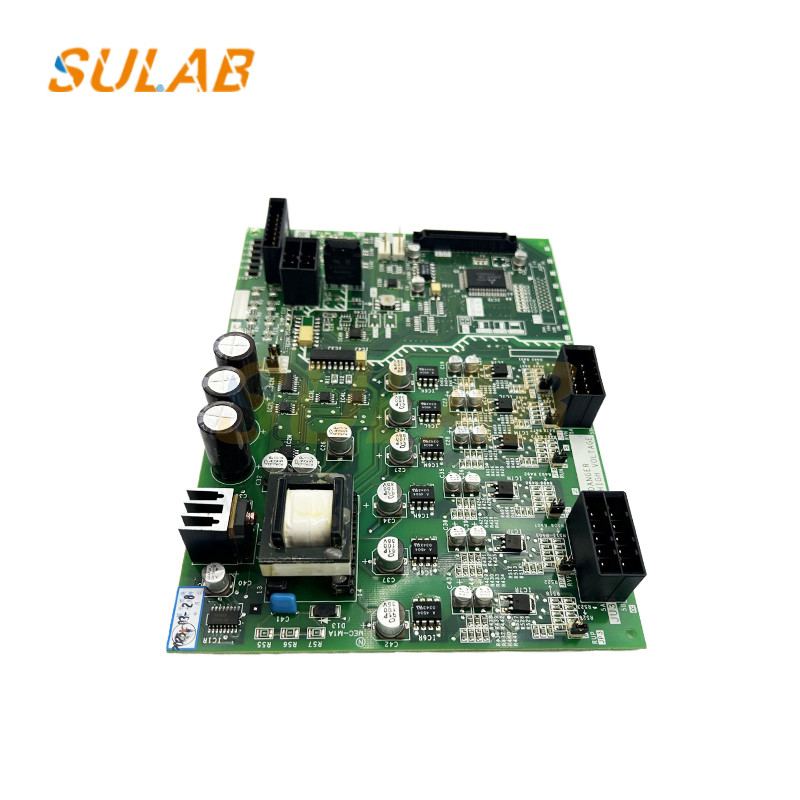
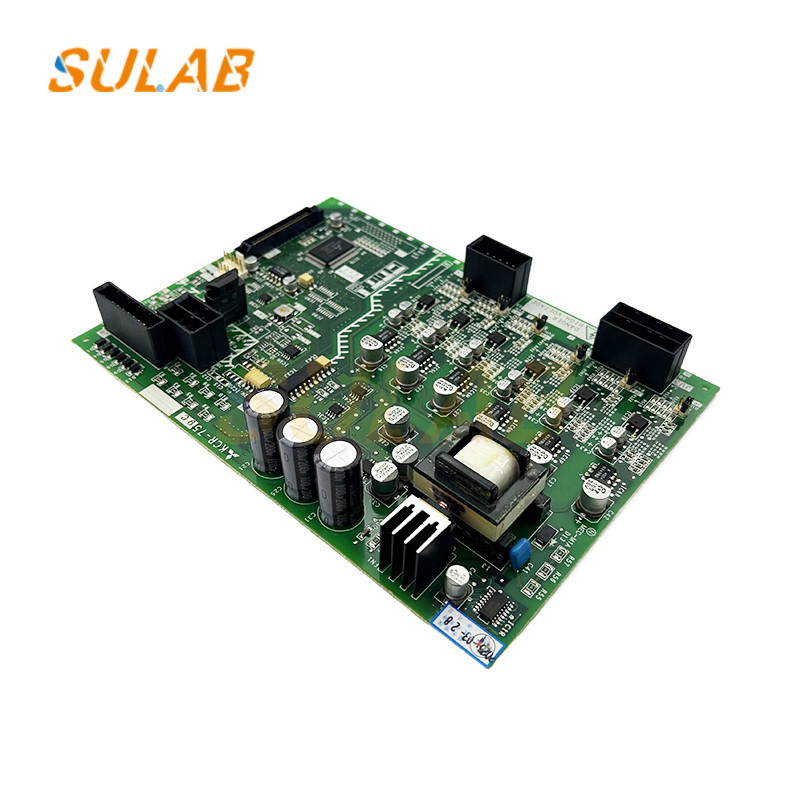
Mitsubishi PCB Board
,Mitsubishi KCR-759C PCB Board
,Elevator PCB Board
-
PackagesCarton, Wooden Case, Pallet Etc
-
Quality100%NEW
-
ConditionNew
-
Product TypeElevator Parts
-
TransportationClients' Requestment
-
BrandSulab
-
DescriptionElevator Parts
-
ModelFB-9B
-
MOQ1PC
-
TransportionTNT, UPS, DHL, Fedex, Air, Sea
-
ApplicableElevator
-
Delivery TimeNormally 2-3 Working Days After Payment
-
WarrantyOne Year
-
Payment MethodCompany Bank, Western Union, Alibaba, Paypal Etc
-
Brand NameMitsubishi
-
Model NumberKCR-759C
-
Minimum Order Quantity1
-
Delivery Time5-8working days
-
Payment TermsL/C,D/A,D/P,T/T,Western Union,MoneyGram
Elevator PCB Board Mitsubishi KCR-759C Elevator Parts
1. General Specifications
-
Model: KCR-759C
-
Application: Elevator control system (likely for door control, signal processing, or motor management)
-
Compatibility: Designed for Mitsubishi elevator models (exact compatibility depends on the series)
2. PCB Design & Manufacturing
-
Layer Count: Likely a 4-6 layer PCB (for signal integrity and power distribution)
-
Material: FR-4 (flame-retardant epoxy laminate)
-
Copper Thickness: 1oz or 2oz (for power handling)
-
Surface Finish: Lead-free HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling) or ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) for corrosion resistance
3. Key Components
-
Microcontroller/Processor: Mitsubishi-specific IC (possibly a proprietary Mitsubishi chip or a Renesas/Microchip-based controller)
-
Power Regulation: Voltage regulators (5V, 12V, 24V DC)
-
Relays/Solid-State Switches: For motor/door control
-
Optocouplers/Isolators: For signal isolation and noise reduction
-
Connectors: High-durability headers for wiring harnesses
-
Protection Circuits: Fuses, TVS diodes, and EMI filters
4. Production Process
-
Schematic & Layout Design – Designed using CAD tools (Altium, Eagle, or Mitsubishi’s proprietary software).
-
PCB Fabrication – Etching, drilling, and layer stacking.
-
Component Sourcing – OEM-approved components (Mitsubishi may use specialized suppliers).
-
SMT Assembly – Automated pick-and-place machines for SMD components.
-
Through-Hole Assembly – Manual or wave soldering for larger components.
-
Testing & QC –
-
In-Circuit Testing (ICT) – Verifies electrical connections.
-
Functional Testing – Simulates elevator operation.
-
Environmental Stress Testing – Checks for vibration/temperature resistance.
-
5. Compliance & Certifications
-
Safety Standards: EN 81-20 (elevator safety), UL/CE (if applicable)
-
EMC Compliance: EN 61000-6-2 (immunity), EN 61000-6-4 (emissions)
6. Common Failure Points & Repairs
-
Burned traces (due to power surges)
-
Failed relays (mechanical wear)
-
Corroded connectors (humidity exposure)
-
Faulty capacitors (electrolytic aging)
7. Replacement & Availability
-
OEM Part: Must be sourced from Mitsubishi or authorized distributors.
-
Aftermarket Alternatives: Rare due to proprietary design.
-
Refurbished Units: Sometimes available from elevator part suppliers.